Hepatic Encephalopathy
4 min read
What is Hepatic Encephalopathy?
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a condition that affects the brain of people who have severe liver disease. Inefficient liver function causes toxins to accumulate in the blood. These toxins can reach the brain and have an impact on brain function.1
Types of HE1
- Acute liver failure (without underlying chronic liver illness) causes type A.
- Some people with shunts connecting two liver veins without underlying liver disease develop type B.
- Cirrhosis, a form of chronic liver disease, causes type C.
Symptoms of HE1,2
Mental:
- Irritation or anxiety
- Thinking difficulties
- Short attention span or trouble focusing
- Changes in personality or mood
- Decreased alertness
Physical symptoms:
- Hands flapping in the air
- Unsteady speech
- Difficulties with sleep
- Worsening of handwriting
- Loss of small hand movements
- Tremors or shaking of hands or arms
- Breath with a musty or sweet odor
Causes and Risk Factors of HE1
The liver struggles to remove natural toxins from the body when you have liver disease. Ammonia and other toxins build up in the blood. The brain can be affected by toxins in the bloodstream temporarily (or occasionally permanently), depending on the toxicity.
- Drinking alcohol
- Several medicines (sleeping aids and antidepressants)
- Constipation
- Either electrolyte imbalance or dehydration
- Bleeding in the digestive tract
- Infection
- Kidney illness
How Does HE Affect Brain?1
Chronic liver illness can cause issues with nervous system such as HE. Toxins produced by the breakdown of food, alcohol, drugs, and even muscles are difficult for a sick liver to remove from the bloodstream. When the liver is not functioning properly, toxins (such as ammonia) can accumulate in the blood and move to the brain, which affects the normal functioning of brain.
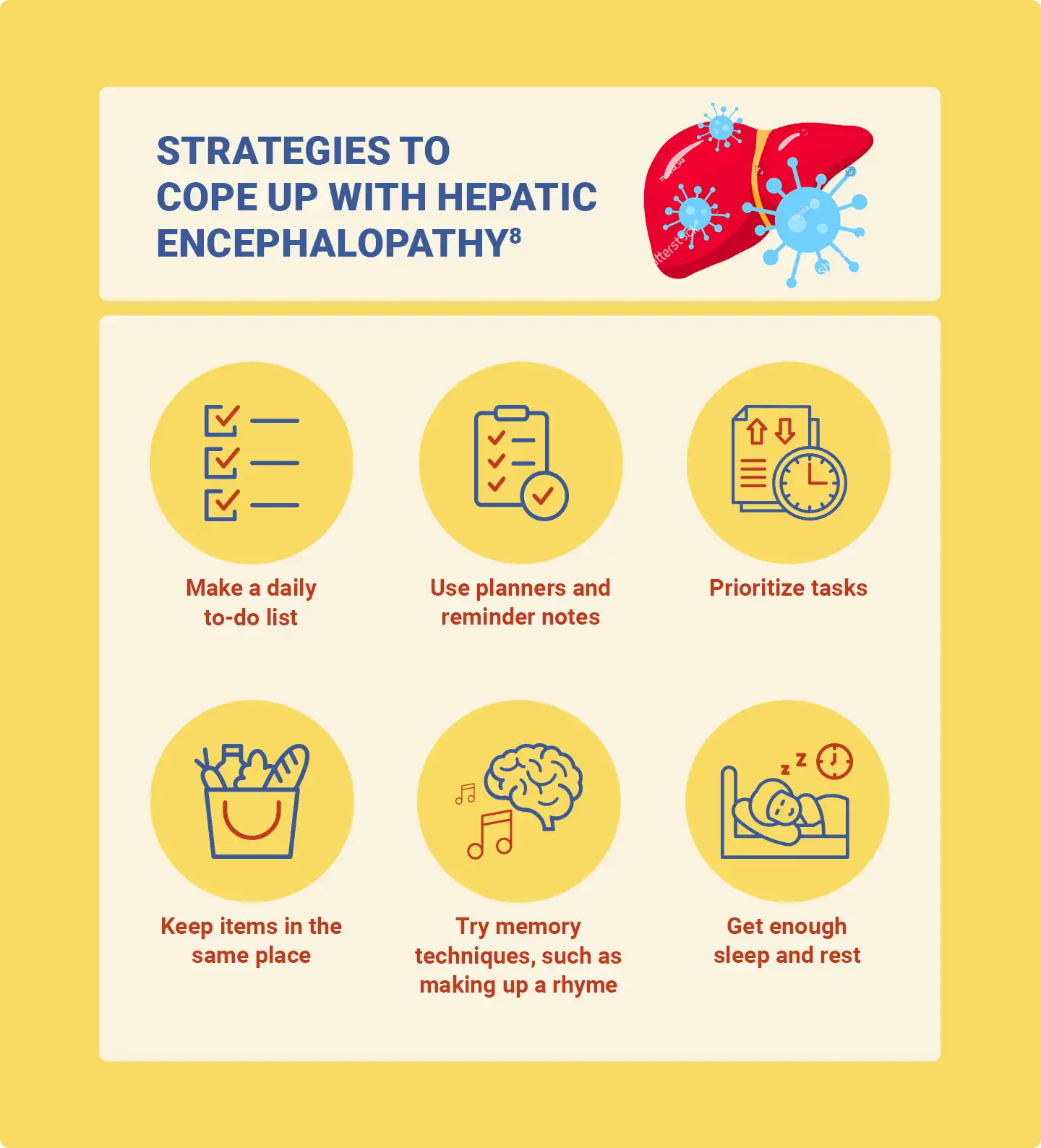
Managing and Preventing HE1,3
Treatment is based on various factors such as the presence or absence of certain symptoms, the severity of the underlying liver disease, and the patient’s age and general health. The management plan includes:
- Elimination of triggers
- Elimination of toxic substances from the intestine
- Antibiotics: Using non absorbable antibiotic, which help to reduce toxin producing bacteria
- Disaccharides: Provide laxative effect that helps to flush toxins from the body
When to Seek Medical Help?4
- Recently, the patient underwent surgery
- While using additional medications, such as sleeping aids, that have an impact on nervous system
- Having an infection recently
- Frequently having problems like dehydration and constipation
Regular Follow-ups with Healthcare Providers1,5,6
- Most patients should undergo baseline nutritional assessment at regular intervals or as directed by a physician
- Patients must be aware that the treatment strategies for HE varies depending on the level of liver damage and the degree of neurological issue
- The progression of HE can be delayed and occasionally even stopped with careful adherence to therapy
- Symptoms of HE can often be resolved with proper treatment and early detection