Navigating the challenges in Constipation
4 min read
Know about chronic constipation1,2
Constipation is defined as having hard, dry stools, or passing fewer than three stools a week. Acute constipation starts suddenly and lasts for a few days. It is usually caused by a change in diet, travel, lack of exercise, illness or medication. Constipation can be considered chronic if you have been experiencing unusual stools or incomplete passage of stools for more than three months.
What are the common symptoms of chronic constipation?2
- Passing fewer than three stools per week
- Hard stools that are difficult or painful to pass
- Straining while passing stools
- Feeling of fullness even after passing stools
Who is at risk of chronic constipation?1
Poor diet and no physical activity are major factors for constipation. You may also be at a greater risk of chronic constipation if you’re:
Age 65 or older – older adults may be physically inactive and have underlying diseases.
Pregnant – changes in hormones and pressure on your intestines from the growing baby can lead to chronic constipation.
Diagnosis of chronic constipation
Many people with constipation often self-treat by changing their lifestyle or using ove-the-counter medications. However, you should consult your doctor if problems continue for more than two weeks.1
The Patient Assessment of Constipation-Symptoms (PAC-SYM) questionnaire for people with chronic constipation:
| Put a tick (√)on the score | |||||
| Symptoms present in the last two weeks | Scores | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| Discomfort in your stomach | |||||
| Pain in your stomach | |||||
| Bloating in your stomach | |||||
| Stomach cramps | |||||
| Painful bowel movements | |||||
| Rectal burning during or after passing stool | |||||
| Rectal bleeding/tearing during or after passing stool | |||||
| Incomplete stools | |||||
| Stools that were too hard | |||||
| Stools that were too small | |||||
| Straining o squeezing to try to pass stools | |||||
| Feeling like you had to pass a bowel movement but you could not (false alarm) | |||||
Score scale: 0=symptom absent; 1=mild; 2=moderate; 3=severe; and 4= very severe
Inference will be based on score scale only. A mean total score in the range of 0-4 is generated by dividing the total score by the number of questions completed. The higher the total score, the higher the symptom burden.
Don’t worry, you are not alone. Speak to your doctor immediately. Your doctor may ask you questions about your symptoms, medical history and any ongoing medications or underlying medical conditions.1 Your doctor may ask you to provide a stool sample for visual inspection and/or additional tests. Your doctor may compare your stools with the Bristol Stool Chart which classifies stool samples according to their shape and form.
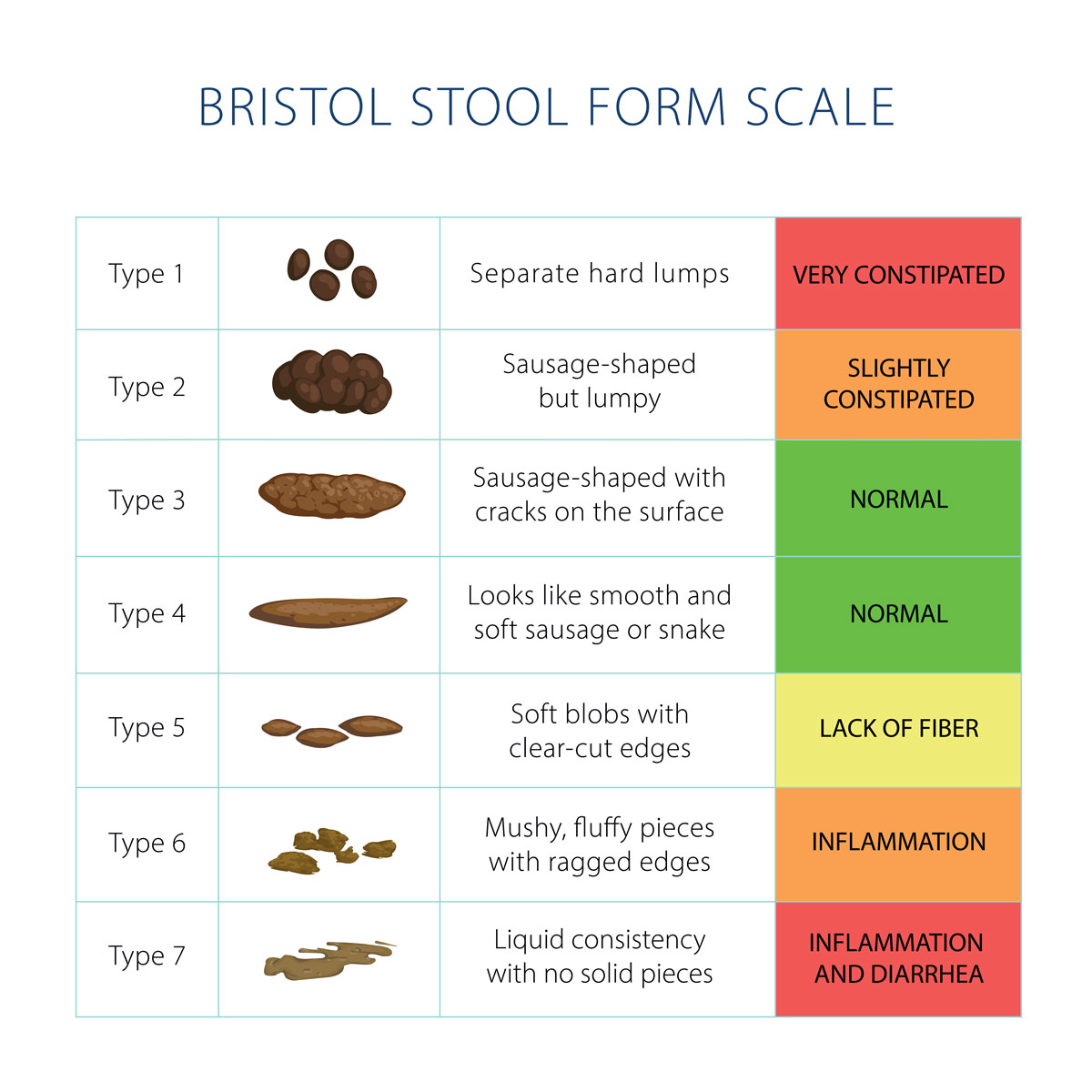
A physical examination may include a digital rectal exam (rectum is the concluding of the large intestine that ends in the anus) and blood tests to check your blood count and thyroid function.1
In severe cases, additional tests may be needed to know the cause of your symptoms. Some of the additional procedures that your doctor may do include colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy.1










