The Ultimate Guide to Sun Protection
4 mins read
Shielding Your Skin for a Healthier You
When you think of sun protection, you probably imagine it is another skincare facade. Who will do so much of the work? But it's much more than that. Protecting your skin from the sun's harmful rays isn't just a beach-day ritual—it's an essential daily habit that helps maintain skin health and prevents long-term damage. Whether out for a morning jog, driving to work, or relaxing at the park, the sun is always around, and your skin deserves its best defense.
Why sun protection is important?1
The sun’s rays contain ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which penetrate the skin, causing various issues—from painful sunburn to premature aging and even skin cancer. Without proper sun protection, your skin is vulnerable to damage that can accumulate over time. Wrinkles, dark spots, and fine lines are not just signs of aging but are often a direct result of too much sun exposure. Beyond the cosmetic impact, consistent unprotected exposure to UV rays can increase your risk of skin cancer. Hence, using sun protection isn't just about beauty or aesthetics—it's about long-term health.
Fortunately, there's a simple and highly effective solution: Sunscreen. One of the most effective ways to combat rising skin cancer rates is through consistent sun protection. Sunscreen plays a key role in defending against both skin cancer and premature aging. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) stresses that while all sunscreens prevent sunburn, only broad-spectrum sunscreens can protect against both skin cancer and early signs of aging.
Broad-spectrum sunscreens: UVA vs. UVB rays2
A good sunscreen will protect you from both UVA and UVB rays, but what's the difference between them?
UVA rays
These are the silent culprits of skin aging. They penetrate deeper into the skin, leading to wrinkles, sunspots, and premature aging. UVA rays are present year-round, regardless of weather, and they can even pass through windows.
UVB rays
These are the ones responsible for sunburn. UVB rays damage the skin's outer layers, causing redness and irritation. While UVB rays are stronger during summer months and at higher altitudes, they are a risk all year long.
For complete protection, it's crucial to choose sunscreens labelled as broad-spectrum to shield your skin from both types of UV rays.
Do I need to protect myself from visible light from the sun?2
Yes! Visible light from the sun can contribute to hyperpigmentation, especially in individuals with darker skin tones. To minimize this risk, it's important to take extra precautions. Start by seeking shade, wearing sun-protective clothing, and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen labelled as "tinted" with an SPF of 30 or higher. Tinted sunscreens are formulated with iron oxide, which has been shown to provide additional protection against the harmful effects of visible light on the skin.
Who should use sunscreen?2
The answer is simple: Everyone. No matter your skin tone, age, or location, sun protection is for all, as you may still be at risk for other forms of sun damage, including hyperpigmentation and skin cancer. Even on cloudy days or in the winter, UV rays can harm your skin, so make sunscreen a daily part of your skincare routine, regardless of the weather.
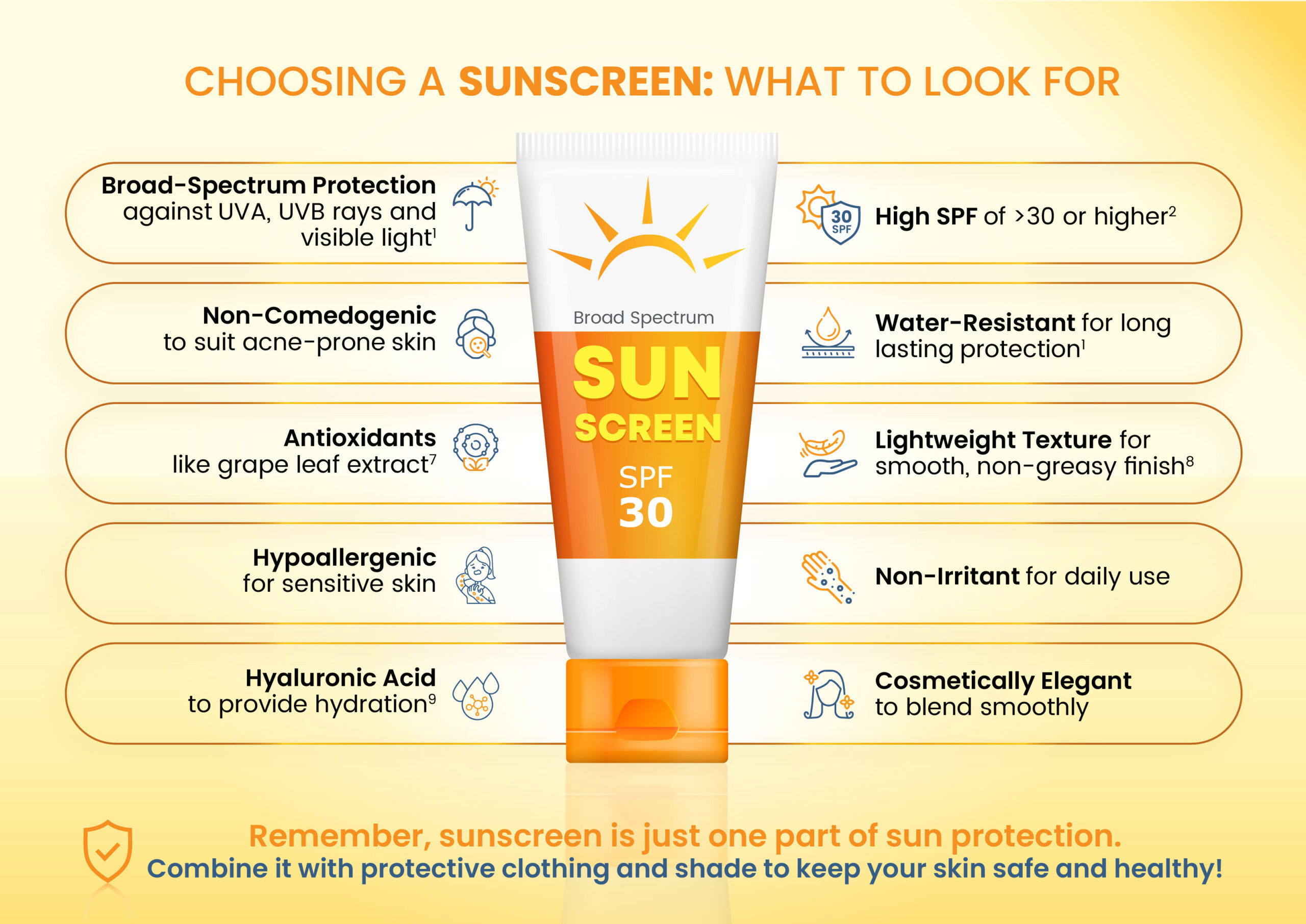
How to read sunscreen labels?1,2
It can be overwhelming to pick the right sunscreen with so many options available. Here's a quick breakdown of what to look for:
Broad-spectrum protection
Look for products labelled as broad-spectrum, which means they protect against both UVA (aging) and UVB (burning) rays. Only sunscreens that meet the FDA's requirements can carry this label.
SPF 30 or higher
Ensure the sunscreen has a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 30. Products that don't meet this requirement must include a warning stating they only protect against sunburn, not skin cancer or premature aging.
Water resistance
Sunscreens may be labelled as water-resistant for either 40 or 80 minutes, indicating how long they protect while swimming or sweating. However, they cannot claim to be "waterproof" or "sweatproof" as no sunscreen fully resists water or sweat.
No instant or extended protection claims
Sunscreens cannot be labelled as "sunblock", nor can they claim instant protection.
How does sunscreen work?3
Sunscreen works by creating a protective barrier on your skin. There are two main types of sunscreens: chemical and physical (or mineral) sunscreens.
- Chemical sunscreens work by creating a thin layer on the skin that absorbs UV radiation before it penetrates.
- Physical sunscreens reflect UV rays away from the skin. These often contain ingredients like zinc oxide or titanium dioxide, which sit on the skin's surface.
Both types are effective, and many sunscreens today combine both chemical and physical ingredients to offer enhanced protection while minimizing side effects. This hybrid approach ensures better defense against both UVA (aging) and UVB (burning) rays, delivering broad-spectrum protection.
How much sunscreen should you use?4
One of the most common mistakes people make with sunscreen is not using enough. For full-body coverage, you need about 1 ounce of sunscreen—that's roughly the size of a shot glass or two tablespoons. For your face alone, a coin-sized dollop or two fingers length is recommended.
How often should you reapply?4
Even if you're not sweating or swimming, sunscreen wears off. Reapply every two hours, or more often if you're in direct sun for extended periods. If you're swimming or sweating, choose a water-resistant sunscreen and reapply immediately after drying off.
Making sun protection a habit
Incorporating sun protection into your daily routine is one of the simplest ways to care for your skin and prevent long-term damage. The key to healthy, youthful skin isn't found in expensive serums or treatments—it starts with daily sunscreen application. Choose a broad-spectrum product, apply it generously, and make it a non-negotiable part of your morning routine. Your future self will thank you!
Top Risk Factors to Avoid for UV Radiation Exposure

Skipping Sunscreen1
1

Not Protecting Your Lips2
2

Ignoring Overcast Days2
3

Neglecting Reapplication of Sunscreen4
4

Prolonged Sun Exposure5
5

Not Wearing Protective Clothing6
6