Unlock the Secrets of Allergic Rhinitis
3 min read
Managing Allergic Rhinitis Effectively
Allergic rhinitis (hay fever) is an allergic reaction to tiny particles in the air called allergens. When you breathe in allergens through your nose or mouth, your body reacts by releasing a natural chemical called histamine. Despite being called hay fever, hay doesn’t cause hay fever and most people don’t get a fever.1
Forms of allergic rhinitis?2
- Seasonal (hay fever): Caused by an allergy to pollen and/or mold spores in the air. Pollen is the fine powder that comes from flowering plants. It can be carried through the air and is easily inhaled. Symptoms are seasonal and usually occur in spring, late summer, and fall. This is the most common form of allergy.
- Perennial: It is caused by other allergens such as dust mites, pet hair or dander, or mold. Symptoms occur year-round.
What causes hay fever (allergic rhinitis)?1
Allergic rhinitis happens when your body’s immune system reacts to an irritant in the air. The irritants (allergens) are so tiny that you can easily inhale them through your nose or mouth.
Allergens are harmless to most people. But if you have hay fever, your immune system thinks the allergen is intruding. Your immune system tries to protect your body by releasing natural chemicals into your bloodstream. The main chemical is called histamine. It causes mucous membranes in your nose, eyes and throat to become inflamed and itchy as they work to eject the allergen from your body. Allergic rhinitis comes from many allergens, including:- Dust mites that live in carpets, drapes, bedding and furniture.
- Pollen from trees, grass, and weeds.
- Pet dander (tiny flakes of dead skin cells).
- Mold spores.
- Cockroaches (their saliva and waste).
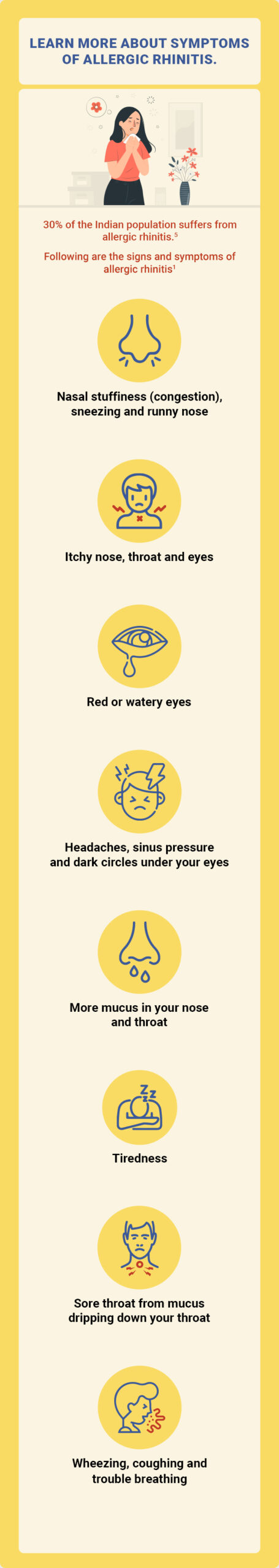
Symptoms3
People with allergic rhinitis generally experience symptoms after breathing in an allergy-causing substance such as pollen or dust. When a sensitive person inhales an allergen, the body’s immune system may react with the following symptoms:
- Stuffy nose due to blockage or congestion
- Runny nose or postnasal drainage
- Itching, usually in the nose, mouth, eyes, or throat
- Red and watery eyes
- Puffy, swollen eyelids
- Sneezing
- Cough
- Cigarette smoke
- Strong odors, such as perfume, or hair spray and fumes
- Cleaning solutions, pool chlorine, car exhaust and other air pollutants (i.e., ozone)
- Air fresheners
How to prevent allergic rhinitis 4

Show References







